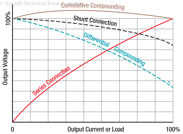
161
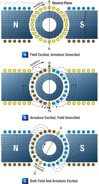
162
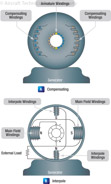
163
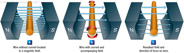
164
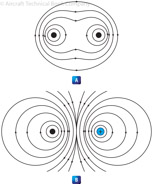
165
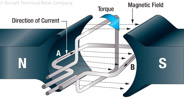
166
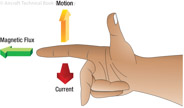
167
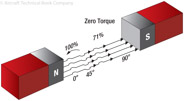
168
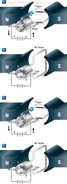
169
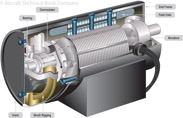
170
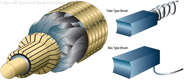
171
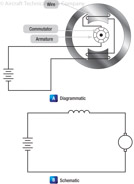
172
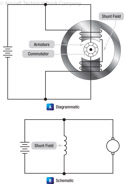
173
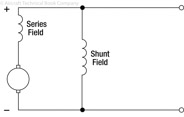
174
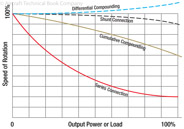
175
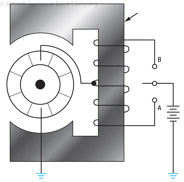
176
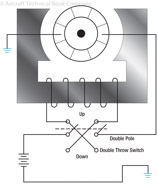
177
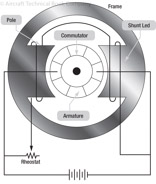
178
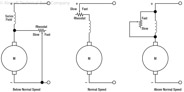
179
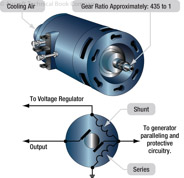
180
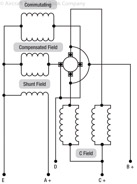
181
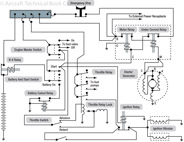
182
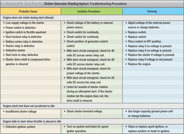
183
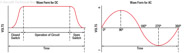
184
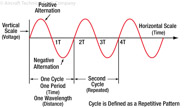
185
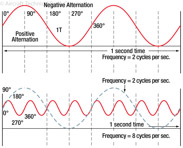
186

187
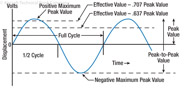
188
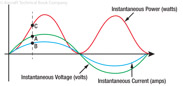
189
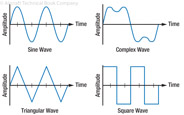
190
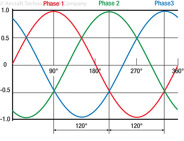
191
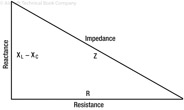
192
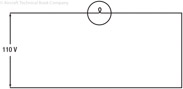
193
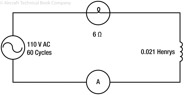
194
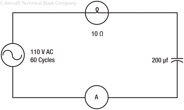
195
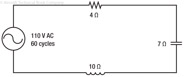
196
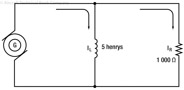
197
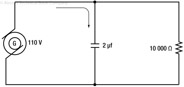
198

199
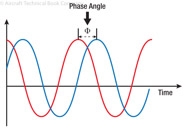
200
